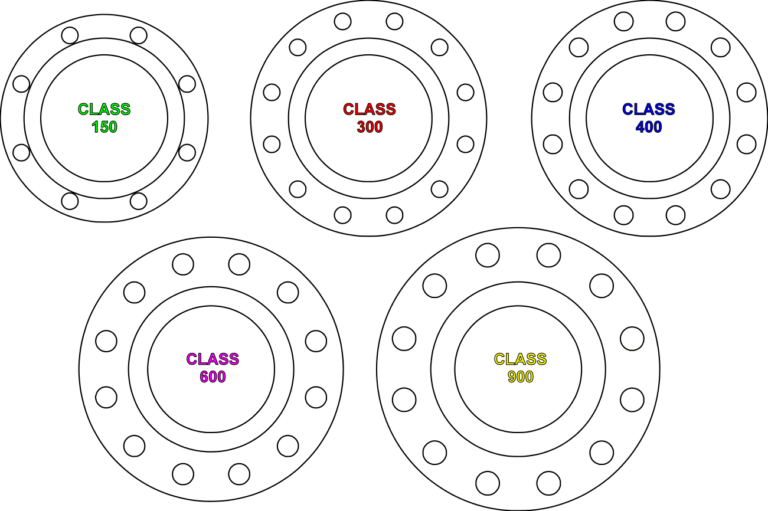
What is a Pipe?
A pipe is a hollow, tube-like structure typically made of materials like metal, plastic, or even clay. Pipes are used to transport fluids, gases, or solids from one place to another. They are commonly used for various purposes, including plumbing to carry water in homes, transporting oil and gas in industrial settings, and even in musical instruments like the organ and bagpipes. Pipes play a fundamental role in our daily lives and are essential for the distribution of essential resources and the operation of various systems and processes.
ASME Standards of Pipe (USA)
ASME covers a wide array of pipe types, each designed for specific applications and conditions. We will explore the various categories of ASME pipes, such as seamless, welded, and more. Additionally, we will discuss the materials commonly used in ASME pipes, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys, and how material selection is critical for different applications.
ASME standards provide a structured approach to pipe sizing, schedules, and dimensions. We will offer a comprehensive guide to understanding ASME pipe sizing terminology, explaining how these designations impact the selection and installation of pipes in different systems.
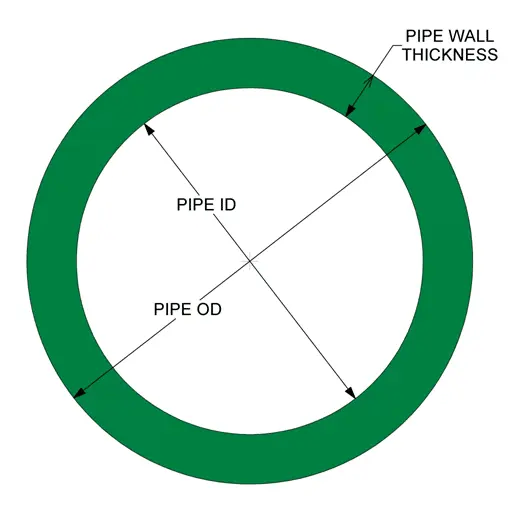
Please follow this Link for Pipe wall Thickness and Schedules:
The manufacturing of ASME pipes is a precision process. This section will delve into the stages involved in producing ASME-compliant pipes, from the selection of raw materials to shaping, welding, and coating. Quality control measures, inspection criteria, and how they adhere to ASME standards will also be discussed.
Different Between Pipe Vs Tube:
Pipes and tubes are both cylindrical structures used in various applications, but they have distinct differences. Pipes are primarily designed to transport fluids or gases. They are measured by their inside diameter (ID) and are typically thicker and stronger to withstand high-pressure applications, such as plumbing and industrial piping systems.
In contrast, tubes are often more versatile, serving as structural components or conduits for heat exchangers and mechanical applications. Tubes are measured by their outside diameter (OD) and are generally thinner with precise dimensions. This makes them more suitable for applications where exact measurements and surface finish are critical.
The choice between pipes and tubes depends on the intended use. Pipes are ideal for fluid and gas transport, while tubes excel in structural and mechanical applications. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the right component for a given task, ensuring efficiency and safety.
Different Types of Pipe Materials:
Each type of pipe is designed for specific purposes. In this discussion, we will explore some of the most common types of pipes, their materials, and their applications.
- Steel Pipes:
Steel pipes are among the most popular and versatile types. They come in various grades and can be used for a wide range of applications, from transporting water and gas to structural purposes. Their durability and strength make them suitable for both underground and above-ground installations.
ASTM Pipe Material Grades – Carbon Steel
API 5L Pipe Material Grades – Carbon Steel - Stainless Steel Pipes:
Stainless steel pipes are known for their resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from food processing to chemical industries. They are durable and can withstand high and low temperatures. - Aluminum Pipes:
Aluminum pipes are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They are often used in industries such as aviation and automotive for their strength-to-weight ratio. - Copper Pipes:
Copper pipes are known for their excellent heat conductivity and resistance to corrosion. They are often used in plumbing systems to carry potable water. Copper pipes are also used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. - PVC Pipes:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They are commonly used in plumbing for drain and waste systems and are also used for irrigation and underground electrical conduit. - PEX Pipes:
PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene) pipes are known for their flexibility and ease of installation. They are used in plumbing for both hot and cold water supply. PEX pipes are often used in residential applications due to their cost-effectiveness and durability. - Cast Iron Pipes:
Cast iron pipes are known for their durability and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used for sewage and wastewater systems. While newer materials like PVC have gained popularity, cast iron pipes are still found in older infrastructure. - HDPE Pipes:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are known for their strength and resistance to chemicals and corrosion. They are commonly used in industrial applications for transporting chemicals and water. Their flexibility and durability make them suitable for underground installations. - Galvanized Steel Pipes:
Galvanized steel pipes are steel pipes coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. They are often used in outdoor and corrosive environments. However, over time, the zinc coating can wear off, leading to potential issues. - Ductile Iron Pipes:
Ductile iron pipes are used for water and sewage systems due to their strength and durability. They are a modern alternative to traditional cast iron pipes and offer a longer service life.
Each type of pipe has its unique characteristics and is selected based on the specific needs of a project. Factors such as material, size, and application determine the choice of pipe to ensure efficient and safe fluid transportation. Understanding the properties and applications of these different pipe types is crucial for engineers, plumbers, and professionals across various industries.