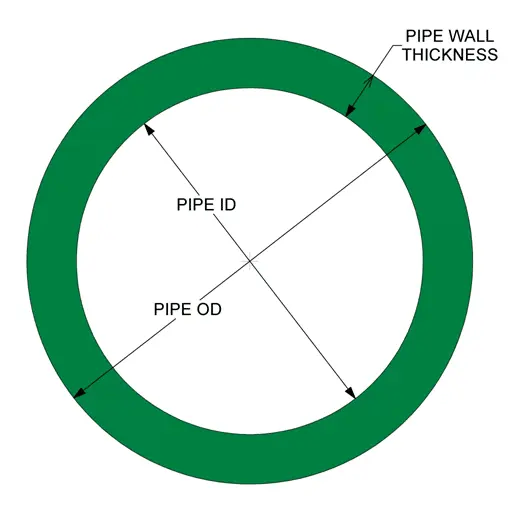
Role of ASTM in Pipe Material Grade:
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) pipe material grades and standards play a pivotal role in ensuring the quality, performance, and safety of pipes used across various industries. These standards provide a common language for manufacturers, engineers, and regulators, facilitating the seamless production and implementation of pipes.
ASTM A53, A106, SA333, and many more are prime examples of these standards. Each grade specifies the characteristics of the pipe material, such as chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing procedures. For instance, ASTM A53 is widely used for carbon steel pipes intended for mechanical and pressure applications, while ASTM A106 is more focused on high-temperature services.
These standards guide the selection of suitable materials for diverse applications, from plumbing to heavy industrial processes. Engineers and manufacturers refer to ASTM standards to ensure that pipes meet the required specifications for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Pipe Manufacturing Methods & Abbreviations:
Pipe manufacturing methods vary depending on the material, size, and intended use of the pipes. Here are some common methods for manufacturing pipes:
| wdt_ID | Item No. | Manufacturing Procedure | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Electric Resistance Welding | ERW |
| 2 | 2 | High-Frequency Welding | HFW |
| 3 | 3 | Submerged Arc Welding | SAW |
| 4 | 4 | Double Submerged Arc Welding | DSAW |
| 5 | 5 | Seamless Extrusion | SE |
| 6 | 6 | Continuous Welded | CW |
| 7 | 7 | Spiral Welded | SW |
| 8 | 8 | Extruded Plastic Pipes | EPP |
| 9 | 9 | Coiled Tubing | CT |
| 10 | 10 | Centrifugal Casting | CC |
| 11 | 11 | Mandrel Mill Process | MMP |
| 12 | 12 | Reinforced Thermosetting Resin | RTR |
| 13 | 13 | Glass Reinforced Epoxy | GRE |
| 14 | 14 | Continuous Filament Winding | CFW |
1. ASTM/ASME A53:
The ASME A53 specification, also known as ASTM A53, is a widely used standard for steel pipes. It outlines the requirements for seamless and welded carbon steel pipes intended for various applications. Here’s a closer look at what makes ASME A53 important and how it impacts the industry.
ASME A53 categorizes pipes into three grades: A, B, and C. Grade A is suitable for low-pressure applications, while Grade B and Grade C are used for higher pressure and temperature services. The choice of grade depends on the specific needs of the project. The standard also covers dimensions, tolerances, and testing requirements to ensure the quality and consistency of the pipes.
When selecting ASME A53-compliant pipes, it’s essential to consider factors like material grade, size, and intended use. The specification provides a robust framework for manufacturers and engineers to meet industry standards and deliver pipes that perform reliably under various conditions.
This specification covers seamless, welded black and hot-dipped galvanized steel Pipes. It only comes in NPS 1/8 to NPS 26.
| wdt_ID | ASTM Code | Pipe Grade | MFG Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ASTM A53/SA53 | Grade A | Type F (Furnace Butt Welded) |
| 2 | Type E (Electric Resistance Welded) | ||
| 3 | Type S (Seamless) | ||
| 4 | Grade B | Type E (Electric Resistance Welded) | |
| 5 | Type S (Seamless) |
This is how it should be Written When you order or add description to your Drawings:
EX: Pipe, 8 NPS, ERW, ASME B36.10M, ASTM A53, Grade-B, Type E.
2. ASTM/ASME A106:
ASME A106 distinguishes pipes into grades A, B, and C, with Grade B being the most commonly used for its balanced strength and cost-efficiency. Its rigorous specifications include dimensions, tolerances, and material properties, ensuring the pipes can withstand extreme conditions.
The seamless nature of ASME A106 pipes eliminates weak points, making them suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature applications. These pipes play a crucial role in reliable fluid transport and are an essential component in various industrial processes.
This specification covers seamless steel Pipes. It only comes in NPS 1/8 to NPS 48. It comes in 3 different grades:
- ASTM A106, Grade A
- ASTM A106, Grade B
- ASTM A106, Grade C
This is how it should be Written When you order or add description to your Drawings:
EX: Pipe, 8 NPS, Seamless, ASME B36.10M, ASTM A106, Grade-B.
3. ASTM/ASME A333:
ASME A333 classifies pipes into grades 1 and 6, with Grade 6 being the most widely used due to its superior impact resistance. The standard imposes strict requirements on dimensions, mechanical properties, and testing, ensuring the pipes’ reliability in sub-zero environments.
ASME A333’s ability to withstand low temperatures without becoming brittle makes it an indispensable choice for applications in cold climates, where other materials may fail. These pipes facilitate safe and efficient transport of various fluids in challenging conditions.
This specification covers seamless, welded carbon and Alloy steel Pipes intended for use at low temperatures.
| wdt_ID | ASTM Code | Pipe Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ASTM A333/SA333 | Grade 1 |
| 2 | Grade 3 | |
| 3 | Grade 4 | |
| 4 | Grade 6 | |
| 5 | Grade 7 | |
| 6 | Grade 8 | |
| 7 | Grade 9 | |
| 8 | Grade 10 | |
| 9 | Grade 11 |
This is how it should be Written When you order or add description to your Drawings:
EX: Pipe, 8 NPS, Seamless, ASME B36.10M, ASTM A333, Grade-6.
Or: Pipe, 8 NPS, Seamless, Low temp, ASME B36.10M, ASTM A333, Grade-6
These are some of the common carbon steel pipe grades used in various industries based on their specific requirements for temperature, pressure, and service conditions.